In modern green agriculture, organic fertilizer has become the cornerstone of sustainable crop production. For entrepreneurs and agri-businesses, mastering how to granulate organic fertilizer will help you gain more profit. Slow-release organic fertilizer provides a supply of nutrients to plants over an extended period. It reduces nutrient loss and improves soil health. However, the quality of the organic fertilizer is dependent on the production process. Many farmers and fertilizer manufacturers often ask, “how to granulate organic fertilizer” effectively to achieve optimal slow-release performance.
In this article, we will delve into the industrial-scale production line of organic fertilizer, focusing on the complete machinery solution from LANE Heavy Industry. Whether you are a small-scale farmer or a large fertilizer producer, understanding how to granulate organic fertilizer with advanced machinery is key to maximizing crop yields and minimizing environmental impact.
LANE Heavy Industry’s Phosphorus-Rich Organic Manure production line is a fully automated, integrated system designed specifically for producing high-quality organic fertilizer granules. It is the industrial answer for businesses asking how to granulate organic fertilizer reliably and at scale. From raw material handling to final packaging, this line is engineered to handle diverse organic raw materials. We use raw materials like animal manure, crop residues, and industrial organic waste and convert them into a consistent, market-ready nutrient for plants. The design is created to produce a nutrient-rich, slow-release fertilizer suitable for orchards, vegetable farms, and grain crops.
The transformation of raw waste into slow-release granules is a meticulous, multi-stage process. Here is a detailed look at how to granulate organic fertilizer using a professional setup from a LANE production line:

Table: Key Process Control Parameters for Quality Granulation
| Process Stage | Key Parameter | Optimal Range / Note |
| Fermentation | Material Temperature | >60°C to kill pathogens |
| Crushing | Particle Fineness | 80% over 80 mesh for drum granulation |
| Granulation | Moisture Content | ~30% for drum granulation |
| Drying | Air Temperature | ≤65°C to preserve microbial life |
| Final Product | Granule Moisture | ≤8% for stable storage |
To understand how to granulate organic fertilizer, you must familiar with the key machines involved. LANE production line integrates the following equipment:
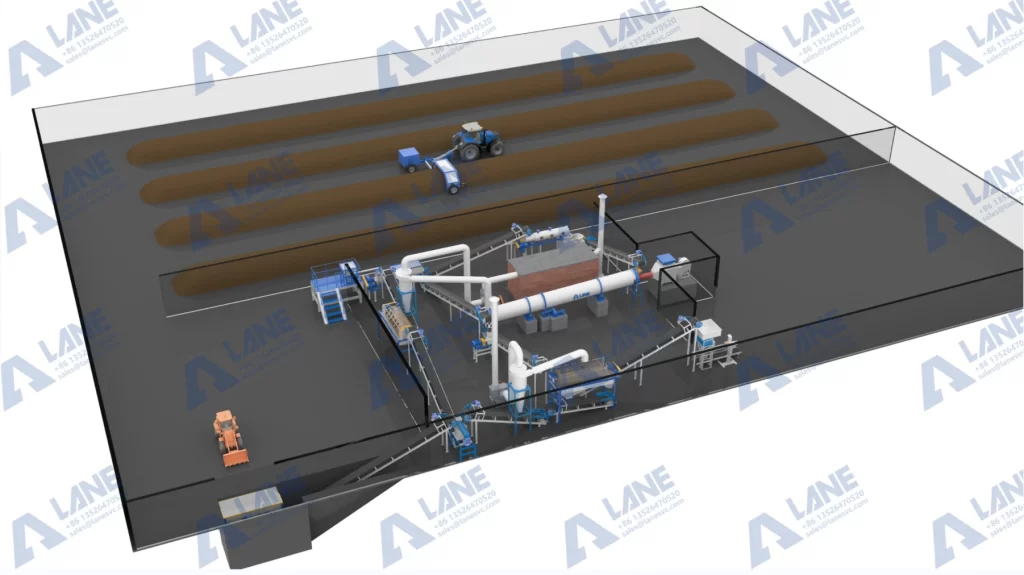
The LANE production line is not just about granulation; it’s about producing a superior slow-release product. Key features include:
Q1: Can the LANE production line handle different raw materials?
A: Absolutely. The line is designed with flexible raw material compatibility. It can process a wide range of inputs, including animal manure (chicken, cow, pig), crop straw, urban organic waste, and industrial bio-waste like vinasse or mushroom substrate. This versatility makes it ideal for producers learning how to granulate organic fertilizer using different feedstocks.
Q2: What is the difference between a disc granulator and a rotary drum granulator for organic fertilizer?
A: Disc granulators are suitable for fine powders but often limit organic content to 30–40% and may require pre-drying. Rotary drum granulators, like those used by LANE, are more versatile for mixed organic-inorganic materials, can handle higher moisture content, offer higher throughput, and are generally more robust for continuous, large-scale production—making them the preferred choice for anyone learning how to granulate organic fertilizer at a commercial scale.
Q3: How do you ensure the fertilizer has slow-release properties?
A: The slow-release effect is achieved through a combination of factors: the inherent slow breakdown of the composted organic matter itself, the addition of mineral carriers like phosphate rock, and the optional post-granulation coating process. The dense structure of the granule, formed under the mechanical action of the drum, also physically slows down the dissolution rate compared to powder, which is crucial knowledge when studying how to granulate organic fertilizer effectively.
Q4: What about after-sales service and support?
A: As a manufacturer, LANE Heavy Industry provides comprehensive support. This includes assisting with workshop layout, dispatching engineers for installation and commissioning, and training on-site workers on how to operate and maintain the granulate organic fertilizer production line. They also offer a warranty and lifelong maintenance service, ensuring clients succeed in producing high-quality fertilizer.
Knowing how to granulate organic fertilizer for slow-release nutrients is essential for running a successful fertilizer business. LANE Heavy Industry’s production line provides a comprehensive, efficient solution. From raw material pretreatment to finished product packaging, each step is optimized for quality, automation, and slow-release performance. By following this how to granulate organic fertilizer guide, farmers and manufacturers can easily master how to granulate organic fertilizer, produce high-quality slow-release products, and achieve better crop yields while protecting the environment.

For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Henan Lane Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520