The environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant is a modern facility designed to convert agricultural waste, livestock manure, and food residues into high-quality granular fertilizers. Unlike chemical fertilizers, which often damage soil health and pollute water sources, organic fertilizers are safer, more renewable, and in line with sustainable agricultural practices.
These factories integrate fermentation, grinding, mixing, granulation, drying and packaging, while maintaining low emissions and minimizing the impact on the environment. By adopting advanced machinery and automation technologies, manufacturers can balance economic benefits and ecological responsibilities.
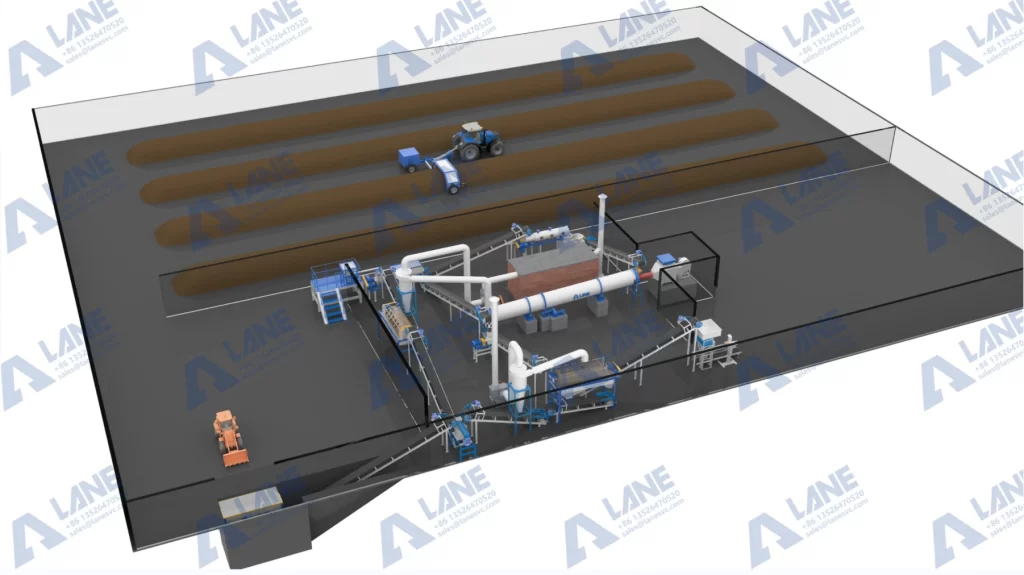
Why Environmentally Friendly Organic Fertilizer Granulation Plant Matters
Sustainable Agriculture: Helps restore soil fertility without relying heavily on chemical inputs.
Waste Recycling: Turns livestock manure, crop residues, and municipal sludge into valuable fertilizer.
Pollution Reduction: Proper composting and processing reduce odor, pathogens, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Economic Opportunity: Farmers and businesses can convert waste into profit.
Global Trends: Governments and consumers increasingly prefer eco-friendly agricultural products.
Workflow of an Environmentally Friendly Organic Fertilizer Granulation Plant
An environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant typically follows a structured process that transforms raw organic waste into stable, nutrient-rich fertilizer granules:
1.Raw Material Collection and Storage
Agricultural residues, livestock manure, food waste, or municipal sludge are collected and stored in designated areas. Materials are sorted to remove non-compostable items like plastics or stones.
2.Composting and Fermentation
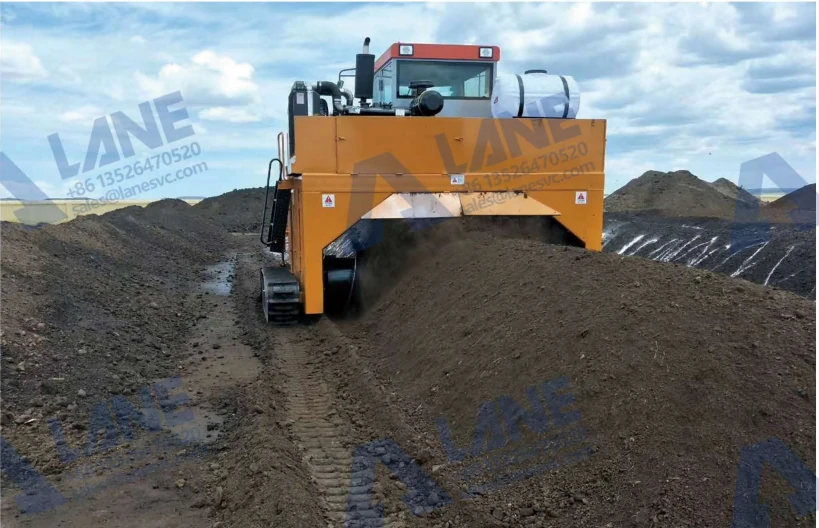
The organic waste undergoes aerobic fermentation using equipment such as the crawler type compost turner or wheel type compost turner. This stage reduces odor, eliminates pathogens, and stabilizes nutrients. Temperature and moisture levels are carefully monitored to ensure thorough decomposition.

3.Crushing and Mixing
After fermentation, the material is often lumpy. A crusher reduces particle size, ensuring that the material becomes uniform and easier to handle in the next processing steps. A horizontal mixer combines fermented material with additives such as mineral supplements, beneficial microbes, or conditioners. This ensures nutrient balance and improves granulation quality. The horizontal design allows even mixing and prevents material buildup.
4.Granulation
The core step transforms mixed materials into granules using equipment such as a disc granulator, rotary drum granulator, or stirring pin granulator. Proper granulation ensures uniform particle size, good density, and improved application efficiency in the field.
5.Drying and Cooling
Moisture is removed in a rotary drum dryer, reducing it to a stable level for storage. Granules are then cooled in a rotary drum cooler to prevent caking and preserve nutrient integrity.
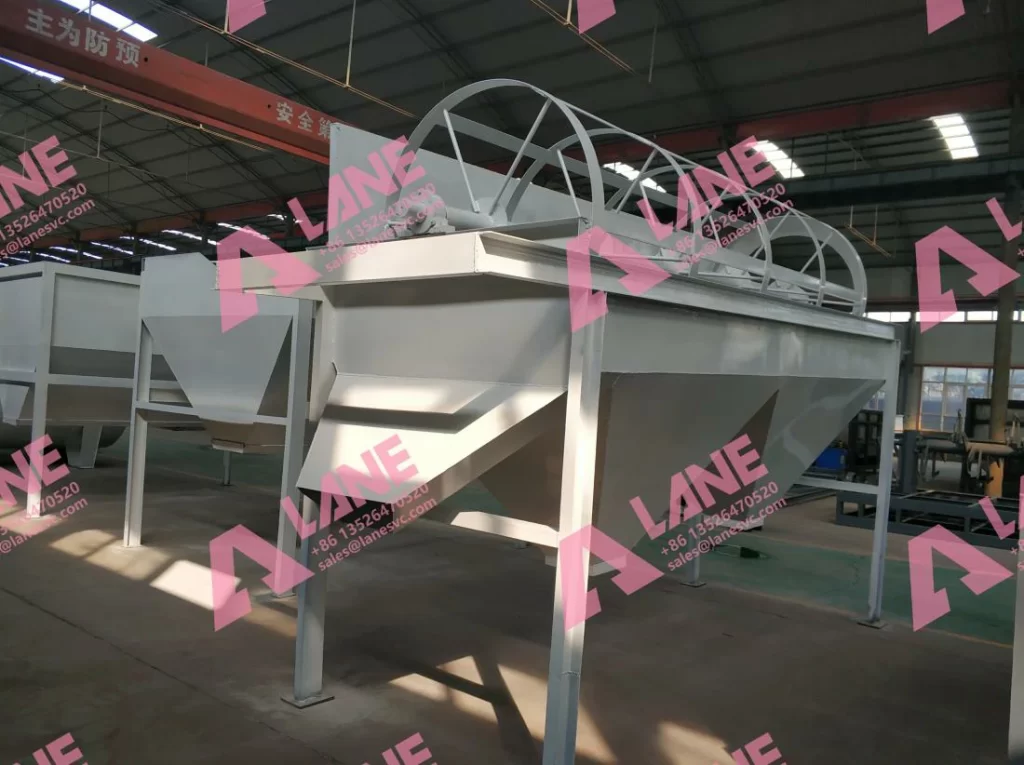
6.Screening and Polishing
Granules pass through a rotary screener to separate qualified products from oversized or undersized ones. A polishing machine may be used to improve granule appearance, making them more attractive for the market.

7.Packaging and Storage
Finally, granules are packed with an automatic packaging system into bags of different sizes. This step prepares the fertilizer for storage, transportation, and market distribution.
This integrated workflow ensures not only high efficiency but also minimal environmental impact, aligning production with sustainable agriculture goals.
Advantages of an Environmentally Friendly Organic Fertilizer Granulation Plant
Sustainable Waste Recycling: Converts livestock manure, crop residues, and food waste into valuable fertilizer, reducing landfill use and pollution.
High Nutrient Retention: Controlled fermentation and granulation preserve nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium while enriching soils with organic matter.
Eco-Friendly Operation: Modern systems minimize odors, dust, and harmful emissions, creating a cleaner production environment.
Improved Fertilizer Quality: Produces uniform, stable, and easily applied granules that enhance soil structure and crop yield.
Automation and Efficiency: Advanced machinery reduces manual labor while increasing productivity and consistency.
Market Competitiveness: Granules are easier to transport and sell, giving producers an advantage in both local and international markets.
Case Study 1: Vietnam’s Integrated Pig and Rice Farm
In northern Vietnam, a large pig farm struggled with manure management, which caused odor issues and polluted local water sources. By investing in an environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant, the farm was able to compost pig manure with rice straw using a crawler compost turner. After fermentation, the mixture was processed with a horizontal mixer, granulated with a rotary drum granulator, and packaged for local sale.
Within one year, the farm reduced waste disposal costs by 35%, generated an additional income stream by selling organic fertilizer to nearby rice growers, and improved community relations by cutting odor emissions significantly. Rice yields in the region rose by 12% after the switch from chemical fertilizers to the locally produced organic granules.
Case Study 2: Brazil’s Sugarcane Residue Utilization
In São Paulo, Brazil, one of the largest sugarcane producers faced challenges with massive amounts of bagasse and filter mud left from processing. Rather than burning or discarding the byproducts, the company built a large-scale organic fertilizer granulation plant to recycle them into high-quality fertilizer.
The process began with composting residues in windrows turned by wheel type compost turners. After fermentation, the material was mixed with mineral additives in horizontal mixers and granulated using stirring pin granulators. A complete drying and cooling line ensured stable products, while automatic packaging prepared them for export.
This approach not only reduced waste disposal problems but also created a profitable new product line. The company now exports thousands of tons of organic fertilizer annually to neighboring countries like Argentina and Chile, while also improving soil fertility in its own sugarcane fields.
Environmental Benefits of Organic Fertilizer Granulation Plants
One of the main reasons why the environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant has gained international recognition is its contribution to environmental protection. Unlike chemical fertilizer factories that rely on synthetic processes and nonrenewable resources, these plants recycle waste materials, lower emissions, and reduce ecological damage.
Odor and Emission Control: Through controlled aerobic fermentation, foul smells are reduced and greenhouse gas emissions are minimized.
Reduced Water Pollution: Proper composting and granulation prevent untreated manure or sludge from entering rivers and groundwater.
Soil Restoration: The organic matter from fertilizer granules improves soil structure, increases microbial diversity, and enhances water retention capacity.
Lower Carbon Footprint: By reusing agricultural residues locally instead of transporting waste, the carbon footprint of farming operations is significantly reduced.
Circular Economy Contribution: These plants close the loop between agricultural production and waste disposal, ensuring resources are reused effectively.
By adopting this model, communities can achieve sustainable waste management while also supporting global climate change mitigation goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What raw materials can be used in this plant?
Livestock manure, crop residues, food waste, municipal sludge, and other organic matter.
Q2: How large should the plant be?
It depends on the waste supply. Plants can range from 5,000 tons/year to over 100,000 tons/year capacity.
Q3: Is odor a problem during production?
With proper composting and equipment like bio-filters, odor can be effectively controlled.
Q4: What are the common granulators used?
Disc granulator, rotary drum granulator, and stirring pin granulator are widely used.
Q5: Can the plant be customized?
Yes. Layout, capacity, and equipment choice can be tailored to meet specific needs.
The rise of the environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant reflects a global shift toward greener, more sustainable agricultural practices. From Vietnam’s pig farms to Brazil’s sugarcane industries, farmers and enterprises alike are learning that waste is not a burden but a resource waiting to be transformed. By applying advanced composting, mixing, and granulation technologies, waste streams are converted into market-ready fertilizer products that improve both soil health and crop yields.
What makes these plants especially valuable is their dual benefit. On the one hand, they serve the environment by cutting down on pollution, minimizing odors, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. On the other hand, they create new economic opportunities, whether in the form of reduced input costs for farmers, additional income from fertilizer sales, or export potential in global markets. In this sense, the technology represents not only a farming solution but also a pathway to broader rural development and economic resilience.
Another key advantage lies in the flexibility of the environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant. Whether set up on a medium-sized family farm or scaled up to serve industrial agribusiness, the system can be tailored to local conditions, waste availability, and crop requirements. Its modular design ensures that producers can start with smaller systems and expand gradually as demand grows.
Looking ahead, the importance of these plants will continue to grow as countries face mounting pressure to reduce reliance on chemical fertilizers, manage agricultural waste responsibly, and meet stricter environmental regulations. Governments, research institutions, and private companies are increasingly supporting projects that encourage organic fertilizer production, recognizing it as a critical tool for sustainable food systems.
In conclusion, an environmentally friendly organic fertilizer granulation plant is not just a production line but a symbol of the transition toward ecological balance and agricultural innovation. By integrating waste recycling, soil improvement, and commercial opportunity, it demonstrates that economic progress and environmental protection can go hand in hand. As more regions adopt these systems, the future of global farming will become cleaner, more resilient, and more sustainable.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Henan Lane Heavy Industry Machinery Technology Co., Ltd.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520